Introduction of hydraulic pump
In modern construction machinery, hydraulic working devices are basically inseparable. Even if the main working devices do not use hydraulic equipment, hydraulic systems are usually required to achieve some auxiliary work, which is closely related to our life and work.
Hydraulic transmission is widely used in various fields, and in hydraulic transmission, the hydraulic pump is the power element, especially in the era of mechanization, it is everywhere, and its importance is self-evident.
A complete hydraulic system consists of five parts, namely power components, actuators, control components, auxiliary components and hydraulic oil.
The function of the actuator (hydraulic cylinder and hydraulic motor) is to convert the pressure energy of the liquid into mechanical energy, and drive the machine to perform linear reciprocating motion or rotary motion.
Control elements (various hydraulic valves) control and regulate the pressure, flow and direction of liquids in hydraulic systems.
Auxiliary components include oil tank, oil filter, sealing ring, pressure gauge, etc. Hydraulic oil is the medium that transmits energy in the hydraulic system, including mineral oil, synthetic hydraulic oil, etc.
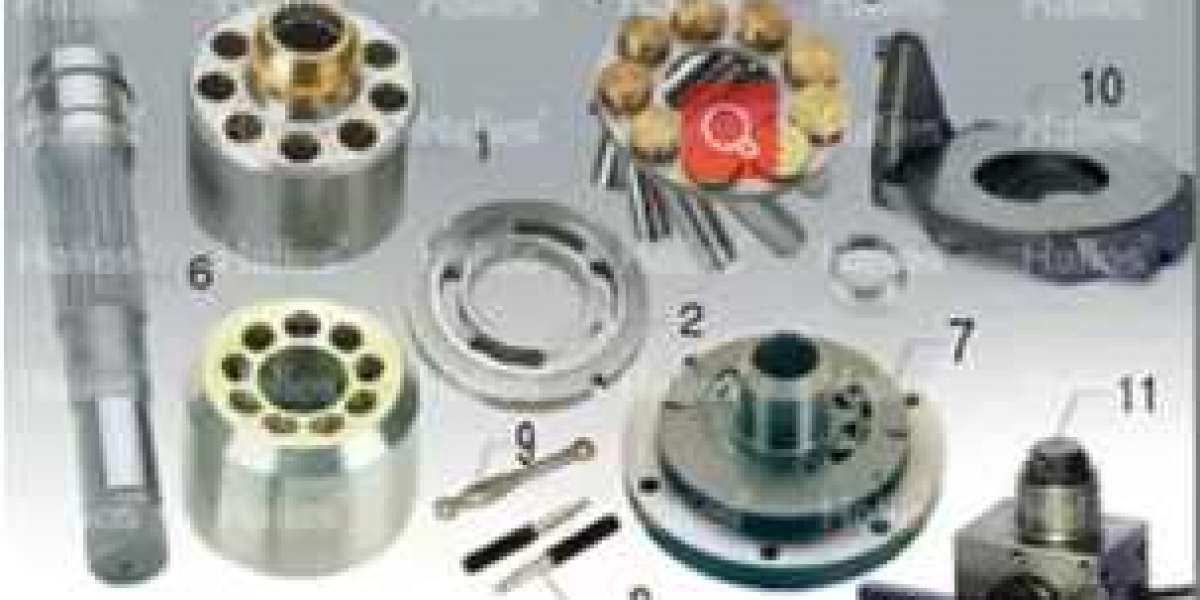
The function of the hydraulic pump is to convert the mechanical energy of the power machine (such as an electric motor and an internal combustion engine) into the pressure energy of the liquid. The output flow can be adjusted according to the needs called variable pump, the flow can not be adjusted called quantitative pump. Although the structures of different types of hydraulic pumps are quite different, there are many commonalities in installation, use and maintenance, and failures may occur if they are not operated properly.
How hydraulic pumps work
The gear pump has the characteristics of small size, simple structure, strong anti-pollution, low price, large leakage, large noise, large flow pulsation, and unadjustable displacement.
The pair of gears rotate with each other, the gear teeth on one side of the meshing teeth gradually disengage, the volume of the sealing cavity increases, and a partial vacuum is formed, and the hydraulic oil in the oil tank is sucked in under the action of atmospheric pressure to fill the increasing volume. The suctioned hydraulic oil fills the tooth slot and rotates with the tooth slot, bringing the oil to the oil pressure chamber on the other side of the meshing area. The two gear meshing lines separate the oil suction chamber and the oil pressure chamber. So that there will be no hydraulic oil leakage between the oil suction area and the oil pressure area, and the gear rotates continuously to complete the oil suction and oil pressure process again and again.
Precautions for hydraulic pumps
When the hydraulic pump is started, it should be jogged several times. After the oil flow direction and sound are normal, run it under low pressure for 5 to 10 minutes, and then put it into normal operation. Before the plunger pump is started, the pump must be filled with clean working oil through the drain port on the casing.
The viscosity of the oil is affected by the temperature, and the viscosity decreases with the increase of the oil temperature. Therefore, the oil temperature is required to be kept below 60 °C. In order to make the hydraulic pump work stably at different working temperatures, the selected oil should have a viscosity Oil temperature characteristics less affected by temperature changes, as well as better chemical stability, anti-foaming properties, etc.
The oil must be clean and free from mechanical impurities and corrosive substances. The hydraulic system without a filter device on the oil suction line must be refueled to the fuel tank by an oil filter truck (filtering accuracy less than 25μm).