What is Forging?
Forging Service is when metal is pressed, pounded, or squeezed under intense pressure to create forgings, which are pieces with high strength. Usually, but not always, the operation is carried out in a heated environment by preheating the metal to the necessary temperature before it is worked. The method of forging is very different from that of casting (or foundry), as the metal used to create forged items is never melted and poured (as in the casting process).
Why use forgings and where are they used?
Stronger pieces can be produced through the forging process than with any other method of metalworking. Forgings are therefore nearly always utilized in situations where dependability and public safety are essential. Forgings are typically found within assembled goods like cars, tractors, ships, oil drilling equipment, engines, missiles, and many types of capital equipment, to name a few, therefore you won't see them very often.
What metals are forged?
It is possible to forge almost any metal. The most popular metals, however, include brass, copper, brass and copper alloys, aluminum, titanium, high-temperature alloys including cobalt, nickel, or molybdenum, and carbon, alloy, and stainless steels. Every metal has different strengths or weights that are best suited for particular portions as chosen by the customer.
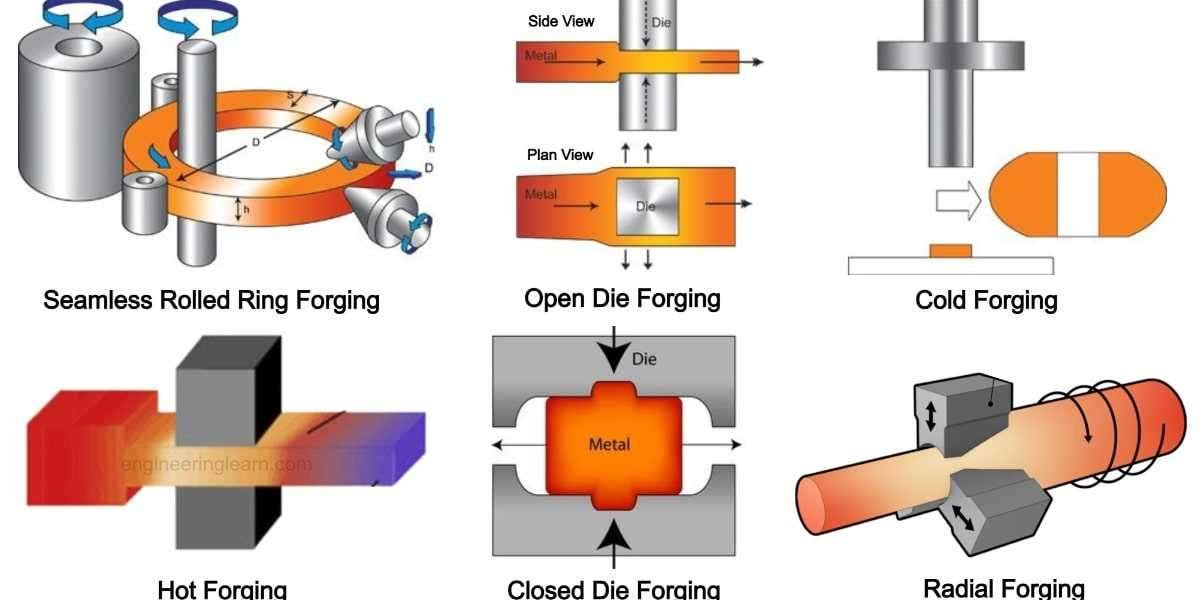
What kind of equipment is used to make forgings?
Any of the following pieces of machinery can make a forging, despite the significant variations in styles and drive systems.
Hammers with a driving force of up to 50,000 pounds use controlled, high-impact strikes to shape the metal.
Up to 50,000 tons of driving power are used in presses to vertically shape the metal under controlled high pressure.
Upsetting is a forging method that uses upsetters, which are essentially horizontal forging presses.
Ring Rollers squeeze out a one-piece ring (without welding) by turning a hollow round piece of metal under great pressure against a spinning roll. required).